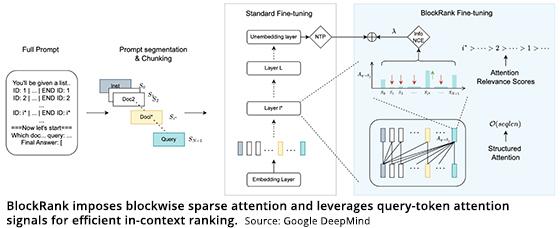
BlockRank, a new ranking model for AI content from
Google DeepMind, is designed to solve a new challenge introduced by artificial intelligence (AI) and large language models (LLMs).
When generative LLMs emerged to search through AI-based
engines, they were required to process enormous amounts of knowledge and demonstrate capabilities in dialogue, responding to questions, reasoning, and other functions to return accurate
information.
Ranking systems needed to change. In-context ranking (ICR) -- the process of having LLMs read multiple documents simultaneously, then determining which content matters most --
was pioneered by researchers at Google DeepMind and Google Research.
The concept, which uses large language models (LLMs) to rank documents based on meaning, was first explored in
2024 and further developed in 2025.
advertisement
advertisement
ICR is expensive and memory-intensive, according to a paper published by Google DeepMind titled Scalable In-context Ranking with Generative
Models.
As the number of documents increases, the input context length grows rapidly. This makes inference computationally expensive and memory-intensive.
Current methods of
ranking, according to the paper, treat the LLM as a black box where ranking systems are hidden.
ICR uses the contextual abilities of LLMs to rank documents by including the task description,
documents, and query in the prompt. It faces efficiency issues such as the ability to rank through what DeepMind refers to as “attention.” This process makes the LLM scale poorly as
the context becomes more complicated and the description adds words.
An experiment with Mistral-7B shows that BlockRank matches or surpasses current methods in both effectiveness and
efficiency, handling up to 500 documents in context quickly.
The ability to retrieve information involves challenges in finding relevant content from a
large document or set of documents. Most retrieval methods are based on word-level matching, which has been done for decades.These systems have
increasingly leveraged deep neutral network-based representations, which achieve their results through an ability to capture deep semantic relationships.
Although it was developed by Google
DeepMind, BlockRank is a research method and not an official Google Search ranking signal.
The technology, which highlights how LLMs and AI are changing the future of search, focuses on a deep
understanding of user intent and the semantic meaning of content The paper explains the process.