
The shelter-in-place, work-from-home dynamic forced by
COVID-19 has steadily increased streaming’s share of total TV time for the past four weeks — driving it up to 23% of U.S. TV households as of the week of March 16, versus just 14% in the
same week last year, according to a new Nielsen Streaming Media data analysis.
Further, the data show that “other” platforms — which now include Disney+ — have
collectively made a significant gain in share against the top four platforms.
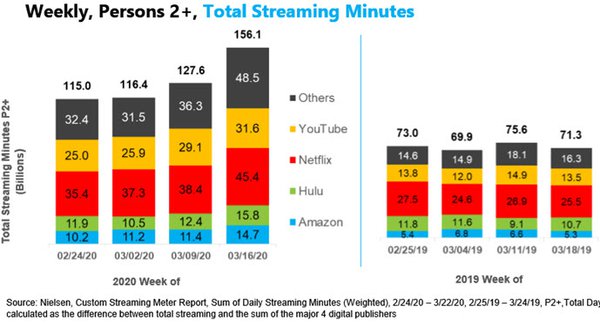
Overall, consumers in TV households with two or more people watched more than 156 billion minutes of
streaming content during that week of March 16. That’s up from 115 billion during the week of February 24, and more than double the minutes during the comparable March week in 2019.
And
while Netflix, YouTube, Amazon and Hulu all saw increases in total streaming minutes per week, comparing the weeks of February 24 and March 16, “other” streaming platforms saw the greatest
jump: up 16 percentage points, from 32.4% to 48.5%.
advertisement
advertisement
By comparison, Netflix was up 10 points, to 45.4 billion minutes; YouTube rose 6.6 points, to 31.6 billion; Hulu rose 3.9 points, to 15.8
billion; and Amazon rose 4.5 points, to 14.7 billion:
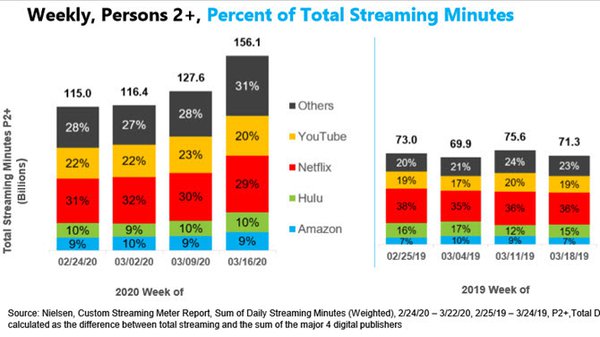
Looking at shares of total streaming minutes,
“other” platforms rose from 28% to 31% between the weeks of February 24 and March 16 this year.
Meanwhile, Netflix and YouTube each saw their shares decline by 2 points.
Compared with the comparable week in 2019, as of the week of March 16 2020, “other” platforms were up by a full 8 points (from 23%). Amazon was up 2 points (to 9%, from 7%).
But
Netflix was down by 7 points (to 29%, from 36%); and YouTube was down 1 point (to 19%, from 20%).
The “other” gains are no real surprise, given that it does include the already
large and rapidly growing Disney+, and that the gains coincide with kids and teens staying at home and “Frozen 2”debuting on Disney+, notes Nielsen. (Disney+ is not yet reported
out by Nielsen.)
Looking at
streaming minutes per week by age demo, the most notable changes during the four recent weeks were an increase of 2.3 points in the age 12-17 group, to 5.3% of minutes, and a 3.7-point decrease in the
15-34 group, to 19.1%.